What The World Cup Tells Us About The Talent Problem In Africa

Pelé famously predicted in 1977 that an African nation would win the World Cup by the year 2000. It probably seemed like a safe bet given the continent’s passion for soccer and the millions of children who grew up playing the game. But it hasn’t happened. The farthest African teams have gotten in the tournament is to the quarter-finals: Cameroon in 1990, Senegal in 2002, and Ghana in 2010. In fact, this year’s World Cup marks the first time since 1982 that no African team has advanced to the knockout stages.
However, players born in Africa but playing for European countries have made lasting impressions on the competition since the 1950s. This year, 14 French players had African roots or connections leading to Trevor Noah’s statement that “Africa won the World Cup” causing much controversy and uproar.
Why do African football players need to leave the continent to experience success?
In order to understand that, we must look at the most commonly cited failures of African teams:
I. Under-funding: Most African children/youth train at the thousands of informal soccer schools across Africa, under the guidance of coaches who often have no formal training and very few resources. There is a lack of high-quality academies offering the kind of training a young player might find in Europe. The shortage of top-notch academies is mainly driven by a lack of resources.
II. Corruption: Lack of funding is further exacerbated by corruption. To highlight a few examples, just as it did with the Olympics in Rio de Janeiro two years ago, Kenya chose to send politicians to Russia for the World Cup, rather than athletes and event organizers, to supposedly learn about the staging of such events! Just before the World Cup, the president of the Ghana Football Association, Kwesi Nyantaki, was caught on film taking a bribe and resigned.
More than $$$$: Lessons for Business
However, money is clearly not all that matters: oil-rich Arab nations are not really much better than the average African nations, despite burning piles of money in building luxury stadiums and hiring foreign players.
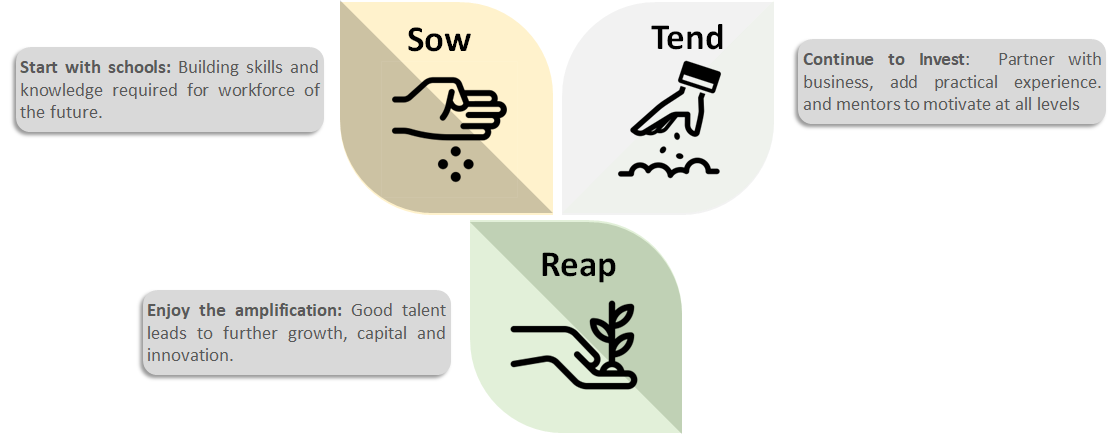
Simon Kuper and Stefan Szymanski looked at the under-performance of African teams in their book Soccernomics. “To win at sports, you need to find, develop and nurture talent,” they concluded. This applies far beyond sports; for Africa to succeed it must focus on talent. Taking Kenya as an example, speak to any organization from start-ups to SMEs to corporates and all will cite talent as a key challenge at all levels. How can African countries successfully develop talent for business? One strategy is the SOW-TEND-REAP:
2. TEND: Continue to invest, working with business to provide practical experiences. Understand what motivates people, what they are trying to achieve and match relevant mentors. Work with governments through policy advocacy, transparency to create an enabling environment for talent and business.
3. REAP: Enjoy the amplification! A talented, motivated work-force is at the heart of any organization or economy. The multiplier effect of growing organizations results in further growth, capital injection, and innovation. This, in turn, leads to a more exciting market which further attracts diaspora leading to reverse brain drain.
To end with a football analogy, for an African team to win the world cup, the Egyptian King Mo Salah is not enough. A cohesive and motivated team, determined to succeed is required. This requires time and investment. For Africa similarly, if we build the talent, growth will follow and in turn attract the diaspora that left to pursue greener pastures.
Note: The view and opinions expressed are of the author’s and does not necessarily represent WeeTracker Media’s Editorial views.